Speaking of financial statements, it’s important that you take the time to review your financial statements on a regular basis. As an owner, you rely on their accuracy to make key management decisions. This can be particularly important for small business owners, who have less room for error.
How are product costs reported in financial statements?
Production costs are usually part of the variable costs of business because the amount spent will vary in proportion to the amount produced. The manufacturer recently received a special order for 1,000,000 phone cases at a total price of $400,000. Being the company’s cost accountant, the manager wants you to determine whether the company should accept this order. Let’s look at a few examples of period costs to illustrate the concept. These do not have a fixed formula as they vary depending on each case.
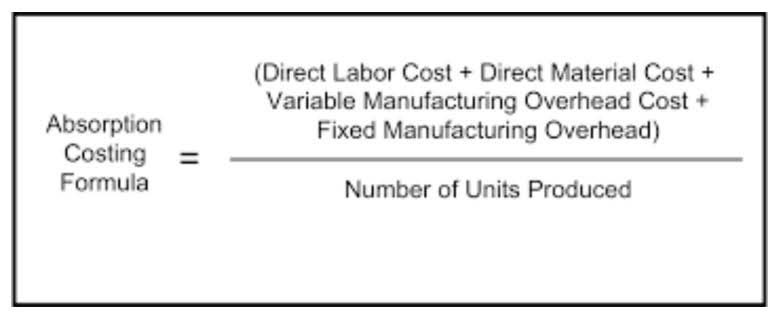
- Examples of product costs are direct materials, direct labor, and allocated factory overhead.
- Sometimes they’re right, but when they’re wrong, the consequences could be disastrous.
- This information can be used to make decisions about where to allocate resources and how to improve efficiency.
- It’s only when the product is sold that these costs are transferred to the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) category on the income statement.
- Product costs help you fine-tune the price of each item you sell, ensuring profitability.
- Advertising, market research, sales salaries and commissions, and delivery and storage of finished goods are selling costs.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
Every cost incurred by a business can be classified as either a period cost or a product cost. A product cost is incurred during the manufacture of a product, while a period cost is usually incurred over a period of time, irrespective of any manufacturing activity. A product cost total period costs is initially recorded as inventory, which is stated on the balance sheet. Once the inventory is sold or otherwise disposed of, it is charged to the cost of goods sold on the income statement. A period cost is charged to expense on the income statement as soon as it is incurred.

LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
You may find yourself in a situation where you determine your production costs are more than you desire. Or, maybe your customers aren’t willing to pay that much for your product. In this case, you may want to consider strategies to reduce product costs. Calculating product costs can be a difficult task, especially when it comes to determining the development costs of SaaS. However, there are some basic formulas to help calculate the product cost.

Impact on the Income Statement

Period costs can be defined as any cost or expense items listed in the firm’s income statement. Both of these types of expenses are considered period costs because they are related to the services consumed over the period in question. Period costs include selling expenses and administrative expenses that are unrelated to the production process in a manufacturing business. Selling expenses are incurred to market products and deliver them to customers.
They are typically incurred during the manufacturing process and may include the cost of direct materials and supplies, factory utilities and equipment setup costs. The wages and benefits paid to workers who are directly involved in production fall into this category, too. Simply put, period costs include any expenses that are not directly related to the production or acquisition of the goods sold.
- Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
- This may seem like an additional cost at first, but quality assurance (QA) is crucial to spotting errors and bugs.
- Remember that retailers, wholesalers, manufacturers, and service organizations all have selling costs.
- On the other hand, if a cost is linked to a product, inventory, production, or goods and may be incurred over several accounting periods, you may be looking at a product cost.
- Recording product and period costs may also save you some money come tax time, since many of these expenses are fully deductible.
Per-unit cost is calculated by dividing your costs by the number of units produced. It is an important metric, particularly when determining product pricing. In some cases, it will be too expensive for a company to eliminate certain types of period costs from its operations. So, as they don’t influence inventory valuation, period costs don’t create confusion about the value of unsold goods.